EDUCATION
The 4Cs
When it comes to defining the quality of a lab grown diamond, you must consider the 4Cs: Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat weight. This criteria helps describe the quality of a mined or lab-grown diamond, and therefore determines its value. Each category has precise definitions set by IGI and GIA. All ROCKRUSH lab grown diamonds come with an IGI or GIA certificate which outlines all 4Cs.
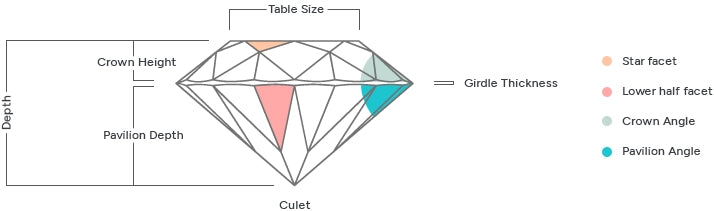
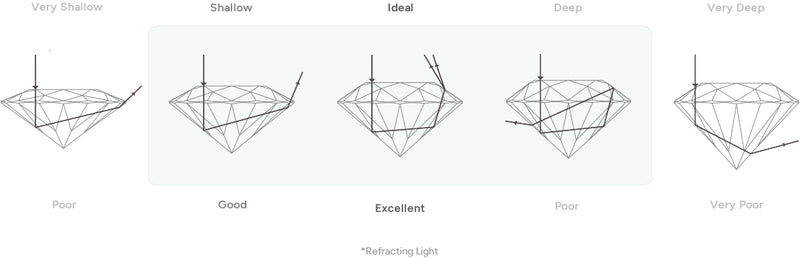
Cut
A lab grown diamond's cut is arguably the most critical factor to consider when buying a lab grown diamond. Why? It's because the cut contributes sharply in giving the lab grown diamond its sparkle. If a lab grown diamond is cut too shallow or too deep, it can lose its play on light.
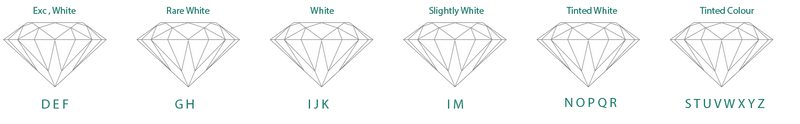
Colour
always refer to the lack of the diamond's colour when grading its whiteness. The highest quality lab grown diamonds are colourless, which can be graded from a scale of D to Z. D represents a colourless diamond and Z refers to a light yellow or brown colour. At the ROCKRUSH y, we carry K+ white lab grown diamonds that provide abundant radiance.
Invisible To The Naked Eye = D-I
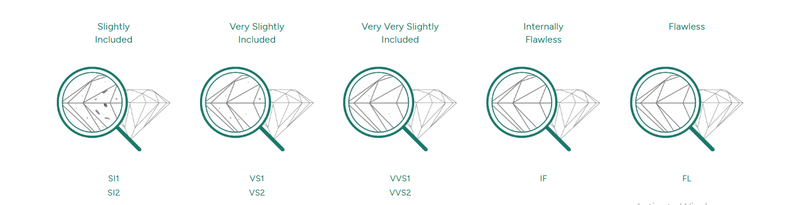
Clarity
A lab grown diamond's clarity refers to imperfections found on the surface or internally. Internal flaws are called inclusions, while external imperfections are referred to as blemishes. The majority of lab grwon diamonds, both mined and lab-grown, feature inclusions and blemishes on a microscopic scale, which is why even lab grwon diamonds with the highest clarity grade feature slight inclusions. At the ROCKRUSH, we reject 60% of all gem-grade lab diamonds, which is a level above the average. The minor inclusions featured in our lab-grown diamonds are entirely invisible to the naked eye.
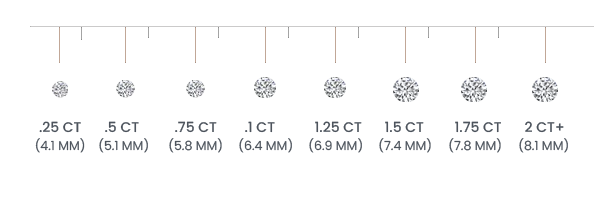
Carat
A Carat refers to a diamond's weight and gives you a sense of its size. The unit of weight for diamonds is the metric carat, which is one-fifth of a gram and is divided into 100 points. A bigger diamond doesn't always mean a more expensive one — you have to consider all the 4 Cs. Here's a tip: When you compare diamond carat sizes, consider a diamond's cut. A high-carat diamond with a poor cut grade can look smaller, often featuring a deeper cut. On the other hand, a diamond with a smaller carat and a sharper cut is always preferable.